Ions arranged by family
Polyatomic cations other than ammonium, hydronium, and mercury(I) aren't
usually encountered in general chemistry.
Most common polyatomic anions occur in "families". All members of the
family share the same central element and the same charge. There are
three common types of variations within the family:
- Different members of the family can have numbers of oxygens.
- Each member of the family can combine with hydrogen ions to
partially neutralize their negative charge.
- Some members of the family can have sulfur substituted for
oxygen.
Other variations exist but are less common.
Table of common polyatomic cations, arranged by family.
Alternate names are given in italics. Select the name of the ion for
information about its occurrence, uses, properties, and structure. Blank
entries are uncommon or unstable; for a complete table see the Field
Guide to Polyatomic Ions.
| carbon |
nitrogen |
sulfur |
chlorine |
|
|
|
CO32- |
carbonate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
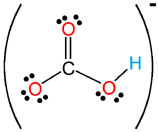
HCO3- |
hydrogen carbonate
(bicarbonate) |
|
|
|
|
NO3- |
nitrate |
|
NO2- |
nitrite |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
SO42- |
sulfate |
|
SO32- |
sulfite |
|
|
|
S2O32- |
thiosulfate |
|
HSO4- |
hydrogen sulfate
(bisulfate) |
|
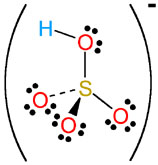
HSO3- |
hydrogen sulfite
(bisulfite) |
|
|
ClO4- |
perchlorate |
|
ClO3- |
chlorate |
|
ClO2- |
chlorite |
|
ClO- |
hypochlorite |
|
| phosphorus |
cyanide |
cations |
metal oxyanions |
|
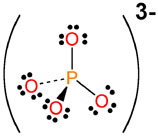
PO43- |
phosphate |
|
HPO42- |
hydrogen phosphate |
|
H2PO4- |
dihydrogen phosphate |
|
|
CN- |
cyanide |
|
OCN- |
cyanate |
|
SCN- |
thiocyanate |
|
|
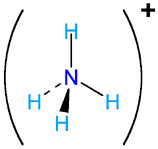
NH4+ |
ammonium |
|
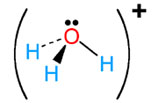
H3O+ |
hydronium |
|
Hg22+ |
mercury(I) |
|
|
CrO42- |
chromate |
|
Cr2O72- |
dichromate |
|
MnO4- |
permanganate |
|
| oxygen |
organics |
|
OH- |
hydroxide |
|
O22- |
peroxide |
|
|
Common naming practices
|
If you can
remember the formula of the ion whose name ends with ate, you can
usually work out the formulas of the other family members as
follows:
| modify stem name with: |
meaning |
examples |
| -ate |
a common form, containing oxygen |
chlorate, ClO3-
nitrate, NO3-
sulfate, SO42-
|
| -ite |
one less oxygen than -ate form |
chlorite, ClO2-
sulfite, SO32-
nitrite, NO2- |
| per-, -ate |
same charge, but contains one more oxygen than -ate
form |
perchlorate, ClO4-
perbromate, BrO4- |
| hypo-, -ite |
same charge, but contains one less oxygen than the -ite
form |
hypochlorite, ClO-
hypobromite, BrO- |
| thio- |
replace an O with an S |
thiosulfate, S2O32-
thiosulfite, S2O22- |
Some anions can capture hydrogen ions. For example, carbonate (CO32-
can capture an H+ to produce hydrogen carbonate HCO3-
(often called bicarbonate). Each captured hydrogen neutralizes one minus
charge on the anion.
| modify stem name with: |
meaning |
examples |
hydrogen
or bi- |
(1) captured H+ ions |
hydrogen carbonate, HCO3- (a.k.a.
bicarbonate)
hydrogen sulfate, HSO4- (a.k.a. bisulfate)
|
| dihydrogen |
(2) captured H+ ions |
dihydrogen phosphate, H2PO4-
|
Table of common polyatomic cations, arranged by charge.
Alternate names are given in italics. Select the name of the ion for
information about its occurrence, uses, properties, and structure.
|
+2 |
|
Hg22+ |
mercury(I) or mercurous |
 |
|
+1 |
|
NH4+ |
ammonium |
|
H3O+ |
hydronium |
|
|
-1 |
|
C2H3O2- |
acetate |
|
ClO3- |
chlorate |
|
ClO2- |
chlorite |
|
CN- |
cyanide |
|
H2PO4- |
dihydrogen phosphate |
|
HCO3- |
hydrogen carbonate or bicarbonate |
|
HSO4- |
hydrogen sulfate or bisulfate |
|
OH- |
hydroxide |
|
ClO- |
hypochlorite |
|
NO3- |
nitrate |
|
NO2- |
nitrite |
|
ClO4- |
perchlorate |
|
MnO4- |
permanganate |
|
SCN- |
thiocyanate |
|
|
-2 |
|
CO32- |
carbonate |
|
CrO42- |
chromate |
|
Cr2O72- |
dichromate |
|
HPO42- |
hydrogen phosphate |
|
O22- |
peroxide |
|
SO42- |
sulfate |
|
SO32- |
sulfite |
|
S2O32- |
thiosulfate |
 |
|
-3 |
|
PO43- |
phosphate |
|
|